Page 242 - Kỷ yếu hội thảo quốc tế: Ứng dụng công nghệ mới trong công trình xanh - lần thứ 9 (ATiGB 2024)
P. 242
th
HỘI THẢO QUỐC TẾ ATiGB LẦN THỨ CHÍN - The 9 ATiGB 2024 233
1. Food Festivals and Markets 5. CONTEXTUAL ANALYSIS OF CHENNAI’S
Example: Marina Beach Food Festival, which TEMPORARY URBAN SPACES
brings together local vendors and chefs to celebrate 5.1. Key Stakeholders in Temporal Urban
culinary diversity and foster social connections (5). Spaces in Chennai
2. Arts and Crafts Events ● Municipal corporations and local governments
Example: Madras Week, an annual event ● Civil society organizations
celebrating the history and culture of Chennai, ● Community leaders and resident associations
featuring arts and crafts demonstrations, music ● Event organizers and promoters
performances, and interactive workshops that
encourage community bonding (5). ● Private developers and property owners
3. Public Art Displays ● Funding bodies and grant providers
Example: Murals and sculptures are installed 5.2. Analysis Of Existing Safety Measures
throughout the city, inviting residents to appreciate ● Regulatory frameworks governing events and
public art and engage in discussions about their gatherings
meaning and significance (5). ● Emergency response plans and protocols
5. Pop-up markets ● Security personnel and crowd control teams
Example: T. Nagar, Parry’sCorner, etc.
● Lighting and visibility improvements
6. Exhibition ● Accessibility and wayfinding signage
Exhibition events in Avadi, flower exhibition in 5.3 Measures for Social Control:
Semmozhi ponga at Chennai, and exhibition stalls in 1. Collaborative Governance: Involving
places like Egmore Museum
stakeholders like communities, governments, and
7. Parking spaces that could be converted for businesses in managing temporal spaces jointly.
other purposes in areas like Mannadi.
2. Clear Guidelines: Establishing rules for usage
8. Temporary Event Venues: to maintain fairness and consistency in managing the
Music concerts and meetings happening in YMCA space.
Ground, and Religious Gatherings such as temple 3. Community Involvement: Engaging the
festivals. community in setting standards and expectations for
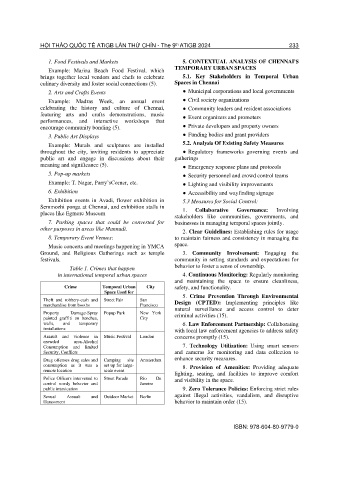
Table 1. Crimes that happen behavior to foster a sense of ownership.
in international temporal urban spaces 4. Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitoring
and maintaining the space to ensure cleanliness,
Crime Temporal Urban City safety, and functionality.
Space Used for
5. Crime Prevention Through Environmental
Theft and robbery-cash and Street Fair San Design (CPTED): Implementing principles like
merchandise from booths Francisco
natural surveillance and access control to deter
Property Damage-Spray Popup Park New York criminal activities (15).
painted graffiti on benches, City
walls, and temporary 6. Law Enforcement Partnership: Collaborating
installations with local law enforcement agencies to address safety
Assault and violence in Music Festival London concerns promptly (15).
crowded area-Alcohol
Consumption and limited 7. Technology Utilization: Using smart sensors
Security, Conflicts and cameras for monitoring and data collection to
Drug offenses drug sales and Camping site Amsterdam enhance security measures.
consumption as it was a set up for large- 8. Provision of Amenities: Providing adequate
remote location scale event
lighting, seating, and facilities to improve comfort
Police Officers intervened to Street Parade Rio De and visibility in the space.
control rowdy behavior and Janeiro
public intoxication 9. Zero Tolerance Policies: Enforcing strict rules
Sexual Assault and Outdoor Market Berlin against illegal activities, vandalism, and disruptive
Harassment behavior to maintain order (15).
ISBN: 978-604-80-9779-0