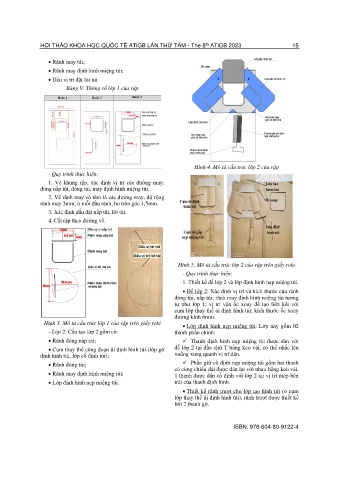
Page 32 - Kỷ yếu hội thảo quốc tế: Ứng dụng công nghệ mới trong công trình xanh - lần thứ 9 (ATiGB 2024)
P. 32
th
HỘI THẢO QUỐC TẾ ATiGB LẦN THỨ CHÍN - The 9 ATiGB 2024 23
Fig. 6. Impact of HHO injection pressure on the
intake manifold's maximum residual H 2 concentration
Fig. 4. Fuel content, HHO, HHO/air ratio, and ϕ in change based on the HHO/air ratio
relation to crankshaft rotation angle a), gasoline
concentration, H 2 and ϕ on intake pipe b), and HHO The relationship between injection pressure and
supply via suction method (n=7500v/min, p=2000Pa) the HHO/air ratio and the highest remaining H 2
concentration in the intake manifold is shown in
3.2. Apply HHO supplements using a injection Figure 6. The maximum H2 concentration that
technique
remains increases quickly when the HHO injection
The H2 concentration contour at position 240ºCA pressure is low, based on the HHO/air ratio that is put
in the engine intake manifold and cylinder is depicted into the cylinder. The HHO/air ratio must not exceed
in Figures 5a, 5b, and 5c. The HHO/air ratio rises 4.75%, 4.5%, and 4%, respectively, with HHO
with increasing injection pressure, resulting in an injection pressures of 3000Pa, 1000Pa, and 500Pa in
increase in the residual H2 concentration in the intake order to guarantee that the highest H 2 concentration
manifold. This is because there is more H 2 that is not does not surpass 1%.
entirely absorbed into the cylinder at the conclusion
of the charging procedure when the HHO
concentration is increased because the injection
process is prolonged. However, the HHO/air ratio Fig. 7. At 240ºCA crankshaft rotation angle, the
rises with an increase in HHO injection pressure concentration of H2 is measured on the intake
while the intake manifold's H2 content stays the same. manifold and in the engine cylinder when the
HHO/air ratio is 3.5% impact of HHO injection
pressure on the intake manifold's maximum residual
H2 concentration change based on the HHO/air ratio
According to Figure 7, which displays the findings
of the simulation, the leftover H 2 content in the intake
channel is negligible at an HHO/air ratio of 3.5%. The
average concentration of residual H 2 on the feed line
is 0.03%, and the equivalency coefficient of the
average residual mixture is only roughly 0.003. The
extremely low ratio reduces the possibility of a
backfire. In order to protect the safety of the HHO
production and supply system, we can select a
minimum HHO injection pressure of roughly 500Pa
when selecting an HHO/air ratio less than 4%.
Fig. 5. Impact of HHO injection pressure on engine 3.3. HHO additional injection solution for a
longitudinal section H2 concentration distribution 110cc Honda Lead engine
based on HHO/air ratio
The research team developed a unique ECU-HHO
set to supply extra HHO for motorcycle engines based
on the outcomes of simulation studies and the design
of the Honda Lead 110cc engine fuel system. The
HHO nozzle control algorithm flow chart (Figure 8) is
followed by the Honda Lead 110cc engine.
ISBN: 978-604-80-9779-0