Page 69 - Kỷ yếu hội thảo quốc tế: Ứng dụng công nghệ mới trong công trình xanh - lần thứ 9 (ATiGB 2024)
P. 69
60 TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC SƯ PHẠM KỸ THUẬT - ĐẠI HỌC ĐÀ NẴNG
Ne = m . Ni = Pe . Vh. i . n = 0,838 . 0,163. 1 . 3600 = 4,1
(kW) 30τ 30 . 4
Effective power (Ne) of the Honda GX160 engine
after improvement:
Ne = m . Ni = Pe . Vh. i . n = 0,8696. 0,183. 1 . 3600 = 4.77
(kW) 30τ 30 . 4
Torque Me of the Honda GX160 Engine:
Ne
Ne
Me = = Ne . 60 ≈ 9,55 (N. m)
ω 2πn n
Where Ne (W) is the effective power, and n (rpm) is
the engine speed.
Me = 9,55 Ne = 9,55 4,1 = 0,01087 (N.m)
n 3600
Torque Me of the Honda GX160 engine after
improvement:
Me = 9,55 Ne = 9,55 4,77 = 0,0126( N.m)
n 3600
There are various ways to increase the compression
ratio of the GX160 engine to suit NH3 fuel, such as
modifying the cylinder head, increasing bore diameter
D, increasing piston stroke, using thinner gaskets, or
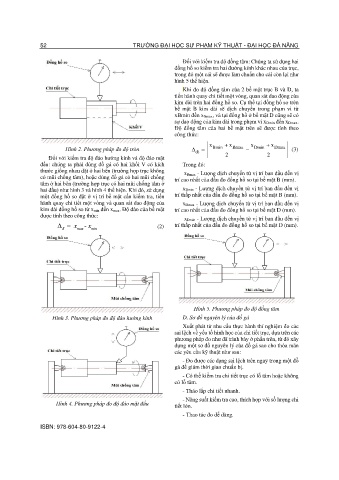
changing the piston shape. In this study, the chosen Figure 2. Piston-Connecting Rod-Crankshaft of the
solution is to increase the piston diameter to raise the Honda GX160 Engine after Modification
engine's compression ratio, without significantly
altering or intervening in the structure of other Based on Figure 1, increasing the compression ratio
components and systems of the engine. To select and leads to a significant rise in engine power. However, in
determine the piston specifications that meet the engine design, the compression ratio is a crucial factor
operating conditions and engine specifications, the for gasoline engines as it directly influences
research team designed a new piston based on the old performance and operation. However, a compression
piston's structure and dimensions, ensuring it is strong ratio that is too high can cause serious issues, such as
enough and does not negatively impact other damage to the piston, cylinder, and gaskets, leading to
components. a reduced engine lifespan. Therefore, to maintain the
compression ratio within the range of ɛ = 10 ÷ 15 while
By keeping other parameters constant and only ensuring engine safety, the case where D=72mm was
changing the piston diameter D, the variations in chosen. The structure and technical specifications of
indicated power Ni , effective power N e , and the Honda GX160 engine after the modification are
compression ratio are illustrated in the graph: shown in Figure 2.
2.3. Power, Pressure, and Reaction Forces
After adjusting the piston diameter to increase the
compression ratio to 10, the modified Honda GX160
engine's indicated power (Ni) increased to 5.545 kW,
up from the initial 4.631 kW. The brake power (Ne) also
rose to 4.77 kW from the original 4.1 kW. Additionally,
the torque (Me) at the crankshaft output saw a
significant increase to 0.0126 N.m, compared to the
initial 0.01087 N.m. These improvements not only
enhanced engine performance but also increased the
engine's load-bearing capacity and efficiency. Notably,
when using NH3 as fuel, the engine demonstrated a
Figure 1. Graph of Ni , Ne , and Compression much better combustion efficiency than before,
Ratio with Varying Piston Diameter contributing to economic efficiency and reducing
environmental impact.
ISBN: 978-604-80-9779-0